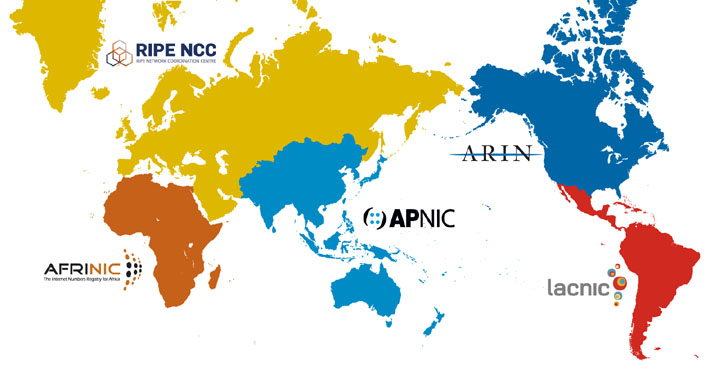
A RIR (or Regional Internet Registry) is a nonprofit organization that allocates Internet Numbers which is comprised of IPv4 Addresses, IPv6 Addresses, and ASN (Autonomous System Numbers) within their respective regions. An IP address is a globally unique number that is assigned to computing devices to communicate with each other within a network (or Internet). ASN is a group of one or more IP prefixes that are used to define routing policy. With IP Address and ASN, IP packets are routed from one IP address to another regardless of where they are located within the world. There are 5 RIRs in the world, and their serving regions:
- AFRINIC: African Network Coordination Centre manages Africa region.
- APNIC: Asia-Pacific Network Coordination Centre manages Asia Pacific region.
- ARIN: American Registry for Internet Numbers manages IP addresses for USA, Canada and many Caribbean and North Atlantic islands.
- LACNIC: Latin American and Caribbean Internet Addresses Registry manages Latin America and the Caribbean.
- RIPENCC: Réseaux IP Européens Network Coordination Centre manages Europe, the Middle East and parts of Central Asia.
Each RIR operates independently and provide services to administer, allocate and register Internet number resources to its members. RIR members are comprised of ISP (Internet Service Providers), governments (countries), education institutions, nonprofit organizations and enterprises.
History of Internet and RIRs
The Internet began as a research project funded by the US Department of Defense to interconnect a small number of computers between universities and research institutions in the 1960s. At that time, researchers haven't anticipated it becoming a global network interconnecting every computing device in the world, and hence defined a 32-bit IP address (IPv4) to uniquely identify an address. However, with the invention of world wide web, emails, smartphones and IoT devices; the Internet became what it is today. As the demand for IP address grow and regions expanded, a 128-bit IP address (IPv6) was invented to supplement the scarce IPv4 addresses and RIRs were formed to administer and allocate the IPv4 and IPv6 addresses to fulfill the growing demand of IP addresses for every individual, organizations, and countries in the world. By delegating IP administrations to 5 RIRs, allocation and distribution of IP numbers are easier and managed efficiently.
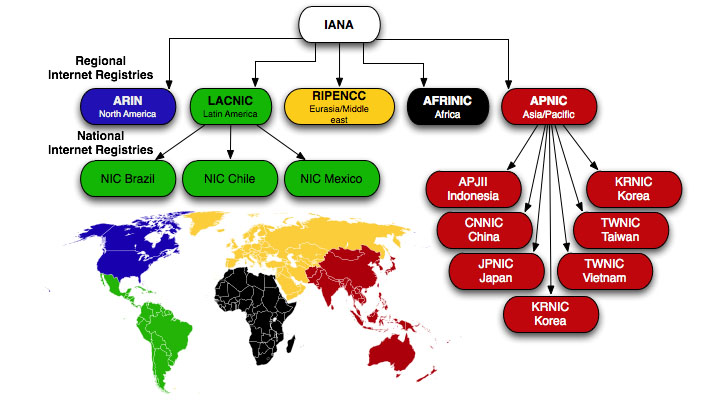
Organizational diagram borrowed from iana.org
What is IANA?
IANA (Internet Assigned Numbers Authority) is a standards organization that oversees the allocation of IP addresses, ASNs, Root Zone management of DNS, protocol assignments, and media (MIME) types. IANA delegates administration and allocation of IP addresses and ASNs to 5 region internet registries.
What is NRO?
Five RIRs formed the Number Resource Organization (NRO) in 2003 to participate in global Internet governance, and aid in policy development to efficiently manage a global pool of IP addresses. The goal of the NRO was to protect the unallocated IP resource pool, fair distribution of Internet numbers to RIRs, and promote transition of IPv4 to IPv6 addresses.
Share this post
Leave a comment
All comments are moderated. Spammy and bot submitted comments are deleted. Please submit the comments that are helpful to others, and we'll approve your comments. A comment that includes outbound link will only be approved if the content is relevant to the topic, and has some value to our readers.

Comments (0)
No comment